Transforming Urban Land Governance: An Intelligence Platform for Ranchi
Leveraging AI and Geospatial Intelligence to Safeguard Public Land and Infrastructure
Understanding the Urban Growth Challenge
Urban expansion and economic development have dramatically reshaped Indian cities, triggering unregulated land use and widespread encroachments on government-owned assets. In Ranchi, like many fast-growing urban centers, vacant public lands have been gradually and often invisibly occupied - undermining urban planning and draining municipal revenues.
Traditional enforcement mechanisms - manual surveys, fragmented records, and reactive interventions - have proven inadequate. Without real-time monitoring and integrated intelligence, city authorities have struggled to secure public lands and maintain orderly urban growth.
The result is not just unplanned expansion. It is rising financial loss, legal disputes, degraded infrastructure, and ultimately, a diminished quality of urban life for millions.
Increased expansion of built up areas in Ranchi in the last 25 years from 9.69% in 1992 to 21.00% in 20171
₹600 crore estimated revenue lost statewide to unrecorded constructions (encroachment).
Manual land surveys cycle every 5 - 7 years - far too slow for a city that can change block‑by‑block in weeks.
Leveraging Intelligence to Transform Urban Land Governance
The Jharkhand Space Application Centre (JSAC) has taken a decisive step toward solving this challenge by developing the Civic Land Area & Infrastructure Monitoring System (CLAIMS) - a fully integrated, intelligence-grade platform purpose-built for municipal land governance.
More than just a mapping tool, CLAIMS fuses:
High-resolution satellite intelligence
AI-driven change detection
Aerial survey integration
Real-time operational dashboards
This system delivers persistent visibility across Ranchi’s urban landscape, enabling authorities to detect unauthorised activity, enforce regulations, and secure critical public assets with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
Built as a scalable, modular platform, CLAIMS is not just a pilot, it is a blueprint for intelligence-led urban management applicable to any fast-growing city across countries.
Key Objectives of CLAIMS
At the heart of CLAIMS is the ability to provide actionable intelligence, enabling Ranchi Municipal Corporation (RMC) to move from fragmented manual processes to a unified, intelligence-led operating environment.
1. Frequent Land Intelligence
Through monitoring powered by high-resolution satellite imagery and GIS-enabled tracking, CLAIMS delivers visibility of land-use changes. Automated alerts surface unauthorised constructions and encroachments the moment they are detected, empowering municipal teams to intervene proactively, not reactively. This intelligence is integrated directly into the city’s enforcement and planning workflows, enabling decisive action to protect public assets.
2. Revenue Integrity through Intelligence
Encroachments don’t just distort city maps, they drain city budgets. CLAIMS provides RMC with the intelligence necessary to optimise revenue streams. By accurately mapping all properties, validating ownership, and detecting unregistered constructions, the system ensures that every taxable asset is brought into the official records. The result is improved property tax compliance, optimised land lease management, and a significant reduction in revenue leakage.
3. Technology-Driven Operations
CLAIMS digitally transforms how urban land governance is executed. Manual, paper-heavy workflows are replaced with a centralised, fully digitised platform, automating approvals, complaint resolution, and enforcement actions under clear, measurable Service Level Agreements (SLAs). By connecting RMC departments, law enforcement, and planners into a shared intelligence environment, CLAIMS ensures accountability, speed, and coordination at every stage of the governance lifecycle.
Operationalising CLAIMS within Ranchi Municipal Corporation (RMC)
CLAIMS is being operationalised as a flagship initiative within Ranchi Municipal Corporation (RMC), with a sharp focus on securing high-value government lands, strategic public spaces, and critical infrastructure corridors, the assets most vulnerable to unauthorised occupation and urban disruption.
The deployment integrates the full intelligence stack:
Satellite Intelligence: High-resolution satellite and remote sensing data provides frequent surveillance, enabling authorities to detect unauthorised constructions and land-use anomalies with precision.
Field-Enabled Intelligence Collection: A mobile application equips field officers with the ability to verify detected changes on-site and report violations directly into the CLAIMS platform in real time, ensuring immediate situational awareness.
Mission-Critical Decision Support: An integrated GIS-powered dashboard offers RMC planners and enforcement teams real-time visualisation, enabling them to identify encroachments, assess their impact, and execute enforcement actions swiftly.
Beyond just a technology deployment, CLAIMS embeds a fundamentally new approach to municipal land governance - one rooted in intelligence, speed, and precision.
By integrating Kompsat-3/3A satellite intelligence, AI-driven change detection, and near-instant operational monitoring, CLAIMS fundamentally disrupts the traditional, reactive model of land governance.
Where manual surveys once took years to detect unauthorised developments - often only after irreversible damage - CLAIMS provides persistent, near real-time visibility.
Where land records were fragmented and verification slow, CLAIMS delivers a centralised, continuously updated source of truth for decision-makers.
This intelligence-grade approach empowers JSAC and RMC to shift from delayed, manual enforcement to proactive asset protection, optimised revenue capture, and data-driven urban growth management - setting a new standard for municipal governance across India and beyond.
- Ramanand Rai, Project Associate
The successful deployment of CLAIMS is anchored by the collaboration between two critical institutions - the Jharkhand Space Application Centre (JSAC) and the Ranchi Municipal Corporation (RMC) - each bringing complementary expertise to deliver a transformational urban intelligence system.
JSAC: Intelligence Backbone and Technology Lead
JSAC serves as Jharkhand's premier geospatial intelligence agency, operating under the Department of Information Technology. Its mandate is to integrate advanced geospatial technologies into governance, infrastructure, and sustainable development.
For CLAIMS, JSAC leads the technical architecture and intelligence capability, contributing:
Satellite Intelligence & Remote Sensing Expertise - Acquisition and processing of high-resolution imagery for land-use and infrastructure monitoring.
AI-Enabled Geospatial Analytics - Development of custom change detection models tailored to urban environments.
Integrated Decision Support Systems - Delivery of GIS-powered platforms designed to streamline planning, enforcement, and policy-making.
JSAC ensures that CLAIMS operates with precision, reliability, and scalability, enabling the system to serve as a persistent source of trusted intelligence for urban governance.
RMC: Operational Authority and Governance Lead
RMC, as Ranchi’s primary urban authority, is responsible for safeguarding the city’s physical and fiscal assets. From land management to taxation, from enforcement to urban development, RMC plays a pivotal role in translating intelligence into action.
RMC's contributions to CLAIMS include:
Urban Planning & Land Governance - Defining zoning regulations, land-use policies, and managing the city’s cadastral database.
Enforcement & Compliance - Executing legal action against unauthorised encroachments and ensuring adherence to building codes.
Revenue Optimisation - Strengthening property taxation and lease management through accurate, intelligence-backed records.
Citizen Engagement - Embedding transparency by integrating grievance redressal and public engagement into the platform.
With JSAC providing the intelligence backbone and RMC operationalising it on the ground, CLAIMS establishes a complete urban intelligence system - closing the gap between data, action, and impact.
The Process
To ensure high-accuracy land monitoring and encroachment detection, the Civic Land Area & Infrastructure Monitoring System (CLAIMS) utilises Kompsat-3 and 3A satellite imagery with a 50 cm spatial resolution. This high-resolution imagery enables precise identification of land-use changes within the 174 sq. km area of Ranchi Municipal Corporation (RMC). The satellite data is acquired quarterly, allowing authorities to detect encroachments and unauthorised land-use changes in a timely manner.
Image Processing and Mosaicking
The first step in processing satellite imagery involves pre-processing and mosaicking to generate a seamless, high-quality base map for analysis. The process includes:
Data Acquisition – The Kompsat-3/3A satellite imagery is sourced quarterly, covering the entire 174 sq. km area of RMC. This data is collected from authorised satellite imagery providers and undergoes quality checks.
Georeferencing and Orthorectification – Raw satellite images are corrected for geometric distortions, ensuring accurate alignment with real-world coordinates. This process eliminates errors caused by satellite tilt, terrain variations, and sensor distortions.
Radiometric Correction – Variations in lighting conditions, atmospheric effects, and sensor inconsistencies are corrected to ensure uniform brightness and contrast across images.
Mosaicking – Since satellite images are captured in segments, individual images are stitched together using advanced mosaicking techniques. This ensures a seamless, high-resolution composite image covering the entire municipal area.
Cloud Removal and Noise Reduction – Any clouds, shadows, or noise in the imagery are detected and removed using AI-based filtering techniques, ensuring clear and accurate imagery for analysis.
Once pre-processed, the final mosaicked image serves as the base layer for further change detection analysis. This high-accuracy reference imagery is then stored in the system’s database for comparison with future datasets.
Change Detection in the CLAIMS System
Once land-use changes and encroachments are detected, the processed data is integrated into the CLAIMS system for visualisation, analysis, and decision-making. The integration process includes:
1. Database Storage & Layer Management –
All detected changes are stored in a central GIS-enabled database.
The system maintains multiple layers of historical imagery, allowing authorities to track encroachments over different time periods.
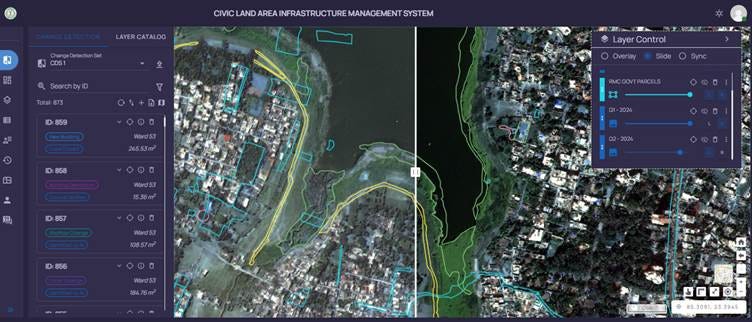
2. Real-Time Visualisation on Dashboard –
The web dashboard displays detected changes using color-coded GIS maps.
Encroachments are marked in red, allowing officials to identify high-risk areas.
Users can toggle between different time periods to analyse land-use evolution.
3. Automated Alerts & Reporting –
The system automatically generates alerts for significant changes, notifying municipal authorities via the web dashboard and mobile app.
Detailed reports are generated, including before-and-after images, GPS coordinates, and classified land-use changes.
4. Legal & Administrative Workflow Integration –
The detected encroachments are directly linked to municipal case management systems.
Authorities can initiate legal action, issue notices, and track the resolution status within the CLAIMS platform.
Change Detection Methodology
To detect land-use changes and encroachments, CLAIMS employs AI-driven change detection algorithms that analyse satellite images over multiple time periods. The methodology includes:
Baseline Image Selection – The most recent quarterly satellite imagery serves as the reference layer, which is then compared with previous datasets to identify changes.
Pixel-Based and Object-Based Change Detection –
Pixel-Based Change Detection: The system compares individual pixels across time-series images to detect even minor variations in land features.
Object-Based Image Analysis (OBIA): The AI model segments the images into land parcels, roads, buildings, and vegetation to identify structural or spatial modifications.
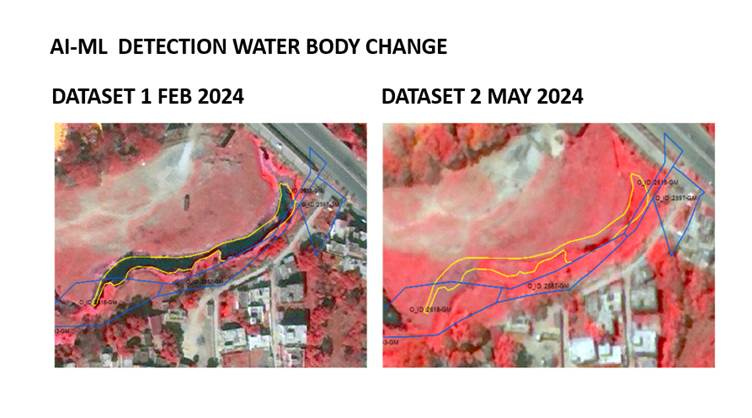
Automated Classification – Using machine learning algorithms, the system classifies detected changes into categories such as new constructions, illegal encroachments, deforestation, waterbody alterations, and infrastructure modifications.
Threshold-Based Analysis – The AI model applies thresholding techniques to filter out false positives (e.g., temporary changes like parked vehicles) and ensure that only significant land-use alterations are flagged.
Change Validation and Post-Processing – To enhance accuracy, the system cross-verifies detected changes with municipal land records, cadastral maps, and field data collected by urban survey teams.
Conclusion: Redefining Urban Land Governance Through Intelligence
The deployment of AI-powered geospatial intelligence through CLAIMS has not only transformed how Ranchi safeguards its public assets - it has redefined what is possible for urban governance itself.
By combining satellite-driven visibility, real-time change detection, and integrated operational workflows, CLAIMS replaces slow, reactive systems with intelligence-led, proactive management. Municipal authorities are now empowered to act faster, enforce more decisively, and plan more sustainably.
This is no longer a vision of the future - it is operational today.
Cities that once accepted land loss, revenue leakage, and inefficient enforcement as inevitable now have a proven model to reverse the trend.
At Aetosky, we stand ready to partner with forward-looking governments and agencies to build the next generation of smart, resilient cities.
https://soeagra.com/iaast/iaastdec2020/4.pdf